What is Private Cloud Architecture: Complete Overview
Private cloud architecture is an increasingly popular approach to cloud computing that offers organizations greater control, security, and customization over their cloud infrastructure. As businesses strive to harness the benefits of cloud computing while addressing specific requirements and compliance regulations, private cloud architecture is a viable solution.
In this article, we will help you to understand private cloud architecture implementation, explore its key components, differentiate between public and private cloud, benefits of private cloud architecture, etc.
What is Private Cloud Architecture?
Private cloud architecture refers to the design and infrastructure of a cloud computing system dedicated solely to one organization. It provides all the benefits of a public cloud, such as scalability, virtualization, and self-service, but with enhanced security and control as it is operated on-premises or within a third-party data center.
Private cloud architecture typically includes a virtualized infrastructure, automated management, and self-service portals, allowing organizations to efficiently deploy and manage their applications and services. With its ability to meet specific requirements, protect sensitive data, and facilitate seamless integration with existing IT systems, private cloud architecture offers organizations a flexible and highly customizable solution for their cloud computing needs.
Why is Private Cloud Architecture important for Businesses?
Private cloud architecture is crucial for businesses due to its numerous advantages. It provides a highly secure and customizable environment that allows businesses to meet their specific requirements and maintain control over their data. With a private cloud, businesses can optimize resource allocation, scale their infrastructure as needed, and improve efficiency and productivity.
It also ensures compliance with strict data privacy regulations and minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Moreover, private cloud architecture enables businesses to strategically align their IT infrastructure with their overall business goals, resulting in enhanced agility and competitiveness in today’s rapidly evolving market.
Understanding Private Cloud Architecture
Private cloud architecture refers to the infrastructure and design that enables organizations to create their cloud-based systems within their own data centers or on-premises resources. It offers the benefits of a cloud environment, such as scalability, flexibility, and self-service provisioning, while providing the control, security, and privacy required by organizations for their sensitive data and applications.
At its core, private cloud architecture is built on a virtualization layer that abstracts physical hardware resources into virtual machines. This virtualization enables the dynamic allocation and management of resources, allowing for elasticity and efficient utilization. The private cloud architecture also includes a self-service portal or interface that enables users to request and provision resources on-demand, without the need for manual intervention from IT personnel.
In addition to virtualization, private cloud architecture incorporates various components such as hypervisors, virtual networks, storage systems, and private cloud management and monitoring tools. These components work together to provide a cohesive and reliable infrastructure for running applications and services. Security is a vital aspect of private cloud architecture, with features like isolation, firewalls, and data encryption ensuring that each user’s data remains separate and protected from other users’ data.
It combines virtualization, self-service provisioning, and various other components to create a scalable, flexible, and secure infrastructure. By understanding the intricacies of private cloud architecture, organizations can effectively deploy and manage their private cloud environments to meet their specific needs and navigate the challenges of modern IT infrastructure.
What are the key Components of Private Cloud Architecture?
Private cloud architecture consists of several key components that are essential for its functioning.
1. Virtualization Layer
One of the main components is the virtualization layer, which allows for the creation and management of virtual machines within the private cloud environment.
2. Management Layer
Another crucial element is the management layer, which provides tools and software for monitoring and controlling private cloud resources. Additionally, the storage layer is crucial for storing and managing data in the private cloud, while the networking layer facilitates communication and connectivity between different components of the private cloud infrastructure.
3. Security Layer
Finally, the security layer ensures the protection of data and resources through authentication, encryption, and other security measures. All these components work together harmoniously to create a robust and efficient private cloud architecture.
4. Software-Defined Infrastructure
In private cloud architecture, software-defined infrastructure (SDI) comes into play. SDI enables the automation and management of infrastructure resources through software, making it easier to deploy, manage, and scale cloud services. It abstracts the underlying hardware, allowing administrators to define and control the entire infrastructure through code.
5. Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration are the backbone of private cloud architecture, eliminating the need for manual interventions and streamlining operations. Automation enables tasks to be performed automatically, while orchestration ensures the coordination and integration of various processes and services. Together, they simplify complex workflows and increase operational efficiency.
How does Private Cloud Architecture work?
Private cloud architecture is a computing model that allows organizations to create their own private and secure cloud infrastructure. It works by virtualizing resources such as servers, storage, and networking within the organization’s data centers. This architecture follows the same principles as public cloud computing, but the infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization and is not shared with other users.
Private cloud architecture typically involves a layer of virtualization software that abstracts the underlying physical resources, enabling dynamic allocation of resources to different applications and users. This allows organizations to have greater control over their data, security, and compliance while still benefiting from the scalability and flexibility offered by cloud computing.
Which Industries Can Benefit from Private Cloud Architecture?
1. Healthcare
Private cloud architecture is highly beneficial for the healthcare sector due to its enhanced security and privacy measures. With the growing reliance on digitalization and the need to store and process vast amounts of sensitive patient data, private clouds offer a secure and controlled environment. This architecture ensures that healthcare organizations have full control over their data, allowing them to define stringent access controls, encryption protocols, and data governance policies.
Furthermore, private clouds enable seamless integration with existing on-premises systems, facilitating the smooth transition of healthcare operations to the cloud while maintaining data privacy and confidentiality.
The private cloud architecture empowers healthcare providers to harness the benefits of cloud computing while adhering to stringent regulatory and compliance standards, ensuring the utmost safety and protection of patient information.
2. Finance and Banking
Private cloud architecture offers many benefits for the finance and banking industry. Firstly, it ensures enhanced security and data privacy, an utmost priority for these sectors. By utilizing a private cloud, financial institutions can keep sensitive customer information within their network, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Private cloud architecture provides greater control and flexibility over data storage and management, enabling financial organizations to efficiently comply with strict regulatory requirements. Moreover, it allows for seamless scalability and operational efficiency, ensuring smooth processing of transactions and high availability of services.
Private cloud architecture empowers the finance and banking industry to safeguard sensitive data, streamline operations, and maintain the highest level of trust and reliability with customers.
3. Government
Private cloud architecture offers numerous benefits for governments, making it an ideal solution for their unique requirements.
Firstly, private cloud architecture enables enhanced security and control over sensitive government data, as it is deployed within the government’s infrastructure. This ensures that data remains within the government’s jurisdiction, mitigating concerns regarding privacy and compliance.
Moreover, private clouds provide scalability and agility, enabling government agencies to rapidly adapt their infrastructure to fluctuating demands. Additionally, private cloud architecture promotes cost-effectiveness by optimizing resource utilization and reducing infrastructure maintenance costs. By leveraging private cloud architecture, governments can streamline their operations, enhance data security, and efficiently utilize resources, improving their overall productivity and service delivery.
4. Education
Private cloud architecture is highly beneficial for the education sector as it provides numerous advantages for schools, colleges, and universities. Firstly, it ensures enhanced data security by enabling educational institutions to store and access sensitive information securely, safeguarding it from any unauthorized access or potential breaches.
Secondly, private cloud architecture offers scalability, allowing institutions to easily expand their infrastructure and capabilities as the demand for digital resources and online learning grows. This scalability also enables educational institutions to optimize their resources and provide seamless and reliable services to students and teachers. Lastly, private clouds in education permit better accessibility, enabling students and teachers to access resources and collaborate from anywhere, on any device, thereby promoting efficient and flexible learning experiences.
5. Manufacturing
Private cloud architecture is highly beneficial for the manufacturing industry due to its inherent advantages.
Firstly, it provides a secure and dedicated environment for storing and processing sensitive data, ensuring compliance with strict confidentiality regulations. By centralizing data storage and management, manufacturers gain improved control over their operations, facilitating efficient collaboration and decision-making.
Additionally, private cloud architecture offers scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to easily expand their infrastructure as their needs evolve, without compromising performance. With reduced downtime risks, enhanced disaster recovery capabilities, and cost-effective IT resource allocation, private cloud architecture proves to be an indispensable tool for manufacturers looking to streamline their operations and boost productivity.
6. E-commerce and Retail
Private cloud architecture is highly advantageous for ecommerce and retail industries. The ability to store and manage enormous amounts of sensitive customer data in a secure and private environment is essential for these sectors, and private cloud architecture provides just that. With dedicated resources and infrastructure, businesses can ensure the reliability, flexibility, and scalability needed to handle the increasing demands of online transactions.
Additionally, private cloud architecture offers enhanced control over data, allowing businesses to comply with various industry regulations and protect customer information. Overall, private cloud architecture empowers e-commerce and retail businesses to efficiently and securely operate, resulting in improved customer experiences and increased business growth.
What are the Benefits of Private Cloud Architecture?
In this section, we will discuss the advantages of Private Cloud Architecture. However, you might face some risks and challenges in migrating to private clouds. These challenges we can discuss in some other blog.
1. Predictable Server Usage
Private cloud architecture can enhance the predictability of server usage through its various features and benefits. Firstly, it allows for increased control and customization of server resources, enabling organizations to allocate resources based on their specific needs and demand patterns. This flexibility ensures that server resources are not underutilized or overburdened, leading to more predictable and balanced usage.
Additionally, private cloud architecture enables automation and self-service capabilities, making it easier to monitor and manage server workloads efficiently. By optimizing resource allocation and streamlining workflow processes, private cloud architecture helps ensure predictable server usage, enhancing overall performance, and maximizing cost-efficiency for organizations.
2. Improved Resource Utilization
Private cloud architecture has revolutionized resource utilization by providing organizations with a flexible and efficient infrastructure. By consolidating servers, storage, and networking resources into a virtualized environment, private cloud architecture enables businesses to effectively utilize their resources, reducing wastage and maximizing efficiency. With the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand, private cloud architecture allows for better resource allocation, ensuring that computational power, storage, and bandwidth are allocated where they are needed the most, resulting in improved overall resource utilization.
Additionally, the automation and self-service capabilities provided by private cloud architecture further enhance resource utilization by allowing users to provision and de-provision resources on-demand, minimizing downtime and unnecessary usage. Thus, private cloud architecture has transformed resource utilization by enabling organizations to optimize and maximize their resources, leading to increased operational efficiency and cost savings.
3. Reduced Costs
Private cloud architecture has revolutionized the way businesses operate, particularly in terms of cost reduction. By providing organizations with the ability to store and access their data and applications securely within their network, private cloud architecture eliminates the need for excessive hardware investment and maintenance costs.
Additionally, it allows businesses to optimize their IT resources by effectively utilizing existing infrastructure and reducing the need for physical servers, resulting in decreased energy consumption and operational expenses. Moreover, private cloud architecture streamlines IT processes, enabling faster deployment and scalability, leading to enhanced operational efficiency, and reducing costs. With these advantages, it is evident that private cloud architecture has significantly improved cost reduction for businesses.
4. Increased Security
Private cloud architecture has played a pivotal role in enhancing security measures within organizations. By implementing a private cloud infrastructure, businesses can enjoy greater control and autonomy over their data, thus minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Private clouds operate on dedicated servers, ensuring that resources are not shared with other entities, further bolstering the security of sensitive information.
Additionally, private clouds enable organizations to customize security protocols based on their specific needs, implementing stringent access controls and encryption methods. With the ability to monitor and control every aspect of data storage and transmission, private cloud architecture has undoubtedly elevated security standards, making it an ideal choice for businesses seeking to protect their valuable assets and maintain the trust of their customers.
5. Regulatory Compliance
The private cloud helps regulate compliance by providing organizations with enhanced control over their data storage and management. By keeping sensitive information within their secure infrastructure, companies can ensure that data privacy and security policies are strictly followed, meeting regulatory requirements.
The private cloud also allows for better monitoring and auditing capabilities, giving organizations the ability to track and document access to sensitive data. In addition, private cloud solutions for businesses enable them to implement strong security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data backup, further ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations. By utilizing private cloud technology, organizations can achieve a higher level of compliance and peace of mind.
6. Legacy Application Compatibility
The private cloud improves legacy application compatibility by providing a flexible and scalable infrastructure that can seamlessly integrate with existing applications. Legacy applications are often built on outdated technology and may face compatibility issues when migrating to modern environments.
However, private cloud environments enable organizations to virtualize their legacy systems, creating a virtual platform that mirrors the existing infrastructure. This makes it easier to manage and update legacy applications while ensuring compatibility with newer technologies.
Additionally, private clouds can leverage tools like containers and APIs to bridge the gap between legacy and modern applications, allowing for a more efficient and streamlined integration process. Overall, the private cloud offers a solution to enhance legacy application compatibility, enabling organizations to modernize their IT infrastructure without sacrificing functionality and stability.
Also Read:The Advantages of Multi-Cloud Strategies
Private vs Public Cloud Architecture
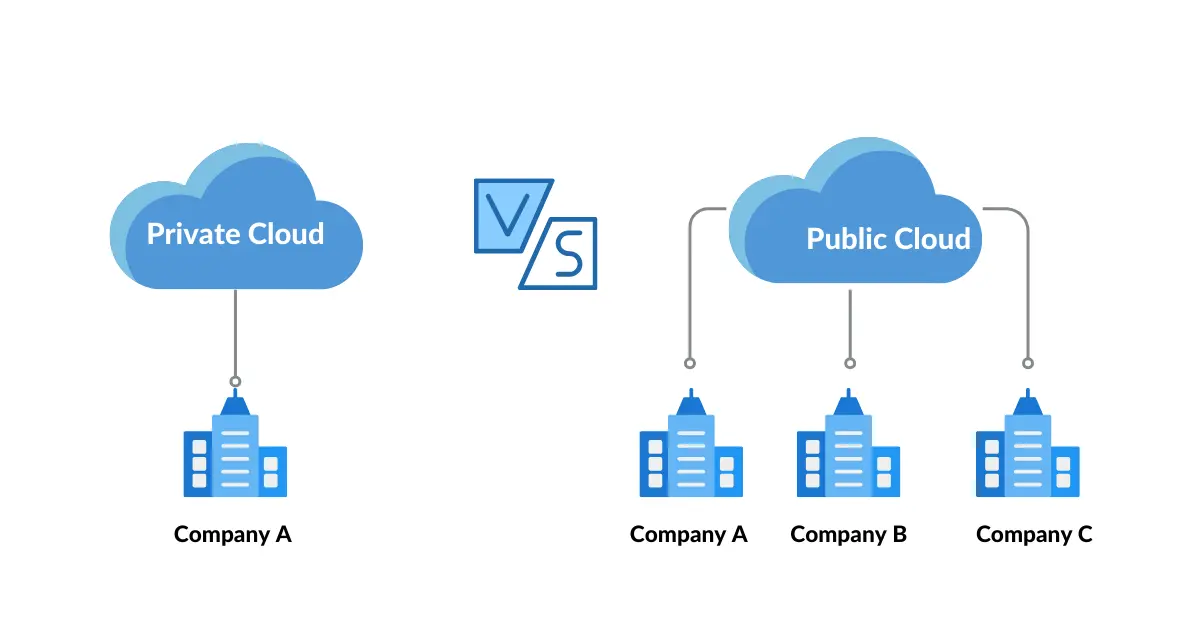
Public cloud and private cloud are two distinct types of cloud computing architectures that offer distinct advantages and features to businesses.
The primary difference between these two architectures lies in the ownership and management of the cloud infrastructure. In a public cloud, the infrastructure is owned and managed by a third-party service provider, while in a private cloud, the infrastructure is owned and operated by the organization itself.
One of the main advantages of a public cloud is its scalability and flexibility. Public clouds can be readily accessed by multiple users and offer unlimited resources and storage capacity. This makes it an ideal choice for businesses with fluctuating demands or those that require burst capacity. Additionally, public clouds are more affordable as they follow a pay-as-you-go model, which allows organizations to only pay for the resources they use.
On the other hand, private clouds offer enhanced security and control. With a private cloud, organizations have sole ownership over the infrastructure and can customize it to meet specific security and compliance requirements. Private clouds are often preferred by organizations that deal with sensitive data or have strict regulatory obligations. Additionally, private clouds provide more predictable performance as resources are not shared with other users, ensuring consistent availability and reliability.
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Owned and operated by a third-party provider | Owned and operated by the organization itself |
| Accessibility | Available to the public or businesses | Restricted access |
| Scalability | Easily Scalable, resources on demand. | Scalability can be limited by hardware. |
| Security | Provider responsible for security. | Organizations have more control over security. |
| Customization | Limited Customizations | High level of customization and control. |
| Compliance | Compliance varies by provider and location. | Easier to meet specific compliance requirements. |
| Maintenance | Provider handles maintenance and updates. | Organization responsible for maintenance. |
| Resource Allocation | Geographically distributed data centers. | Data centers are usually on-premises or hosted. |
| Use Cases | Ideal of variable workloads and startups. | Suited for sensitive data and regulatory. |
Which one is Better for Businesses: Private or Public Cloud Architecture?
When choosing between public and private cloud for businesses, it depends on the organization’s specific needs and preferences. Public cloud offers several advantages such as cost-effectiveness and scalability. It allows businesses to access computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, saving them from making large upfront investments.
With the ability to scale resources up or down as needed, businesses have the flexibility to meet changing demands. Additionally, public cloud providers take care of the maintenance, security, and updates of the infrastructure, reducing the burden on businesses.
On the other hand, the private cloud offers enhanced privacy and control over the infrastructure. It is dedicated solely to one organization and can be located on-premises or managed by a third-party provider. As a result, businesses have more control over data in private cloud security and compliance, which may be crucial for industries with strict regulations. Moreover, the private cloud offers better performance and reliability since resources are not shared with other organizations. It can also be customized to meet specific business requirements, making it an ideal choice for businesses with unique needs or sensitive data.
The choice between public and private cloud for businesses depends on factors such as cost, scalability, privacy, control, and specific requirements. While the public cloud offers cost-effectiveness the private cloud provides enhanced privacy and control. Therefore, businesses should carefully consider their objectives and evaluate the pros and cons of each before deciding. Additionally, a hybrid cloud solution, combining both public and private cloud, can also be considered to achieve the best of both worlds.
Future Trends and Innovations in Private Cloud Architecture
1. Edge Computing and Distributed Private Clouds
Edge computing, which brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, is an emerging trend in private cloud architecture. By distributing cloud resources across multiple edge locations, organizations can reduce latency, improve performance, and enhance data security. This approach enables real-time data processing and enables new applications in areas like autonomous vehicles, IoT, and smart cities.
2. Containerization and Microservices
Containerization and microservices are revolutionizing the deployment and management of applications within private cloud environments. Containers provide lightweight, isolated environments that enable faster application deployment, scalability, and portability. Microservices architecture, built on containerization, allows applications to be divided into smaller, loosely coupled services that can be developed and scaled independently. Embracing containerization and microservices helps organizations achieve agility, scalability, and efficient resource utilization.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Private Clouds
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are reshaping private cloud architecture by enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and data-driven decision-making. These technologies can help in cloud cost optimization, optimizing resource allocation, detecting anomalies, enhancing security, and improving the overall performance of the private cloud infrastructure.
AI and ML algorithms, deployed within the private cloud, can analyze vast amounts of data to extract valuable insights, leading to improved operational efficiency and better user experiences. In conclusion, private cloud architecture offers organizations the flexibility, control, and security required to meet their specific cloud computing needs.
How can OTS Solutions help you with Cloud Migration and Integration services?
OTS assists organizations with cloud migration and integration services. With their expertise and knowledge in the field, OTS professionals can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the entire process. They can help assess an organization’s current infrastructure and applications, determine the best cloud migration strategy, and develop a comprehensive plan for seamless integration.
Additionally, OTS can ensure compatibility and security, as well as optimize the cloud environment to maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging OTS expertise, organizations can achieve a smooth and successful transition to the cloud, enabling them to leverage the numerous benefits of cloud technology.
Also Read: How Cloud Computing Can Help Businesses? A Comprehensive Guide
Conclusion:
Private cloud architecture serves as a secure and flexible solution for organizations looking to manage their infrastructure and resources. By deploying a private cloud, businesses can achieve enhanced scalability, efficiency, and control over their data and applications.
Overall, private cloud architecture enables organizations to harness the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining the security and privacy of their data, making it an ideal choice for businesses seeking to embrace digital transformation and maximize their competitive edge.
Optimize Your Business with Private Cloud Solutions
Ready to scale securely? Our Private Cloud Architecture services provide tailored solutions for your business needs. Experience unmatched flexibility, reliability, and security. Elevate your operations and stay ahead in the digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is the private cloud more secure than the public cloud?
Ans) Private clouds are more secure than public clouds. Moreover, private clouds offer a higher level of control and customization, allowing organizations to implement stricter security measures tailored to their specific needs. Additionally, since private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, the risk of potential data breaches from other entities is mitigated.
2. How does private cloud architecture support regulatory compliance?
Ans: Private cloud architecture supports regulatory compliance by giving organizations complete control and ownership over their data and infrastructure. This enables them to implement strict security measures that meet the requirements set by regulatory bodies.
3. Is private cloud architecture more expensive than public cloud?
Ans) Whether private cloud architecture is more expensive than public architecture depends on numerous factors. Private cloud involves setting up and managing cloud infrastructure within an organization’s premises, which typically requires significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and skilled personnel.
Additionally, ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and security measures can contribute to higher costs. However, as the organization’s needs grow, the cumulative expenses over time might surpass those of a private cloud. The cost-effectiveness of private or public cloud architecture depends heavily on the organization’s specific requirements, long-term goals, and the level of control and security desired.
4. Can private cloud architecture be used for disaster recovery?
Ans) Private cloud architecture can indeed be utilized for disaster recovery purposes. With its focus on providing dedicated infrastructure and resources solely for a single organization, a private cloud offers enhanced security and control compared to public or hybrid cloud options. In the event of a disaster, organizations can rely on their private cloud environment to ensure business continuity, as it offers readily available and scalable computing resources, data storage, and network capabilities.
Related Blogs:
- Which Is Better for Your Business Colocation or the Cloud?
- How to Choose the Right Cloud Consulting Company for Your Business?
- The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Computing: What Your Business Needs To Know.